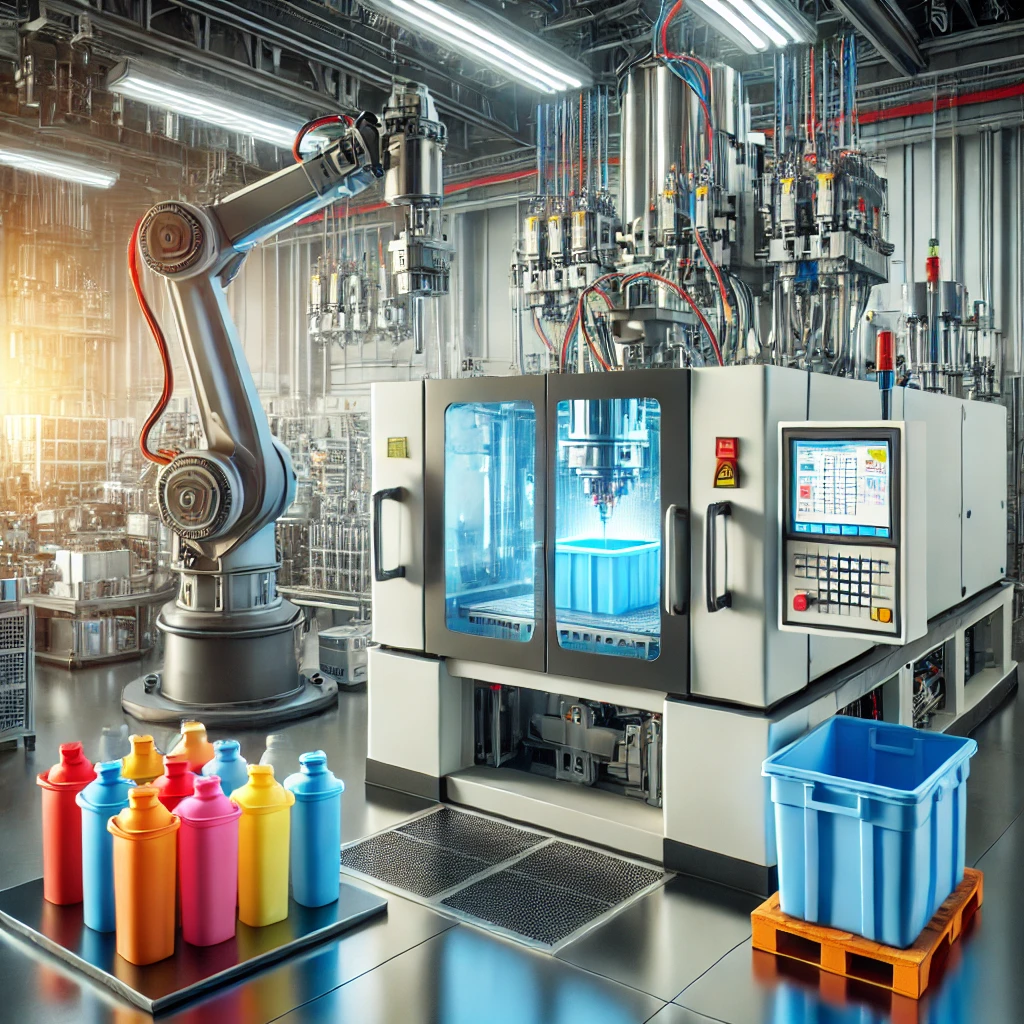
Injection blow molding process(IBM) is a method used to create hollow plastic products. It combines the precision of injection molding with the efficiency of blow molding. This technique is ideal for producing containers, bottles, and jars. Let’s delve into the details of the process, its advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
Modern Injection Blow Molding Process
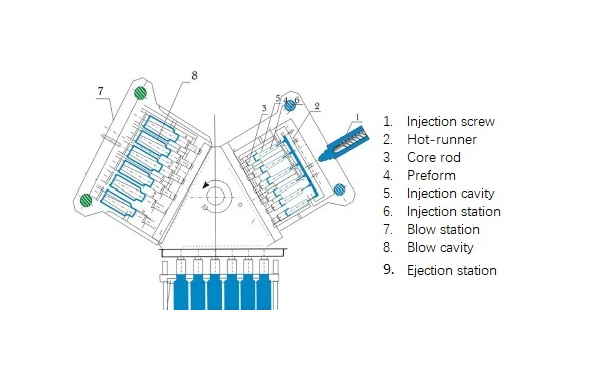
In modern injection blow molding (IBM), the entire process occurs on a single machine. This reduces the need for manual intervention and enhances productivity. The machine consists of three main stations: This integration enhances efficiency, precision, and automation.

- Injection Station
- Blow Mold Station
- Ejection Station
Detailed Steps in the Advanced Process
First, let’s explore the detailed steps involved in the advanced IBM process.
- Injection Station:
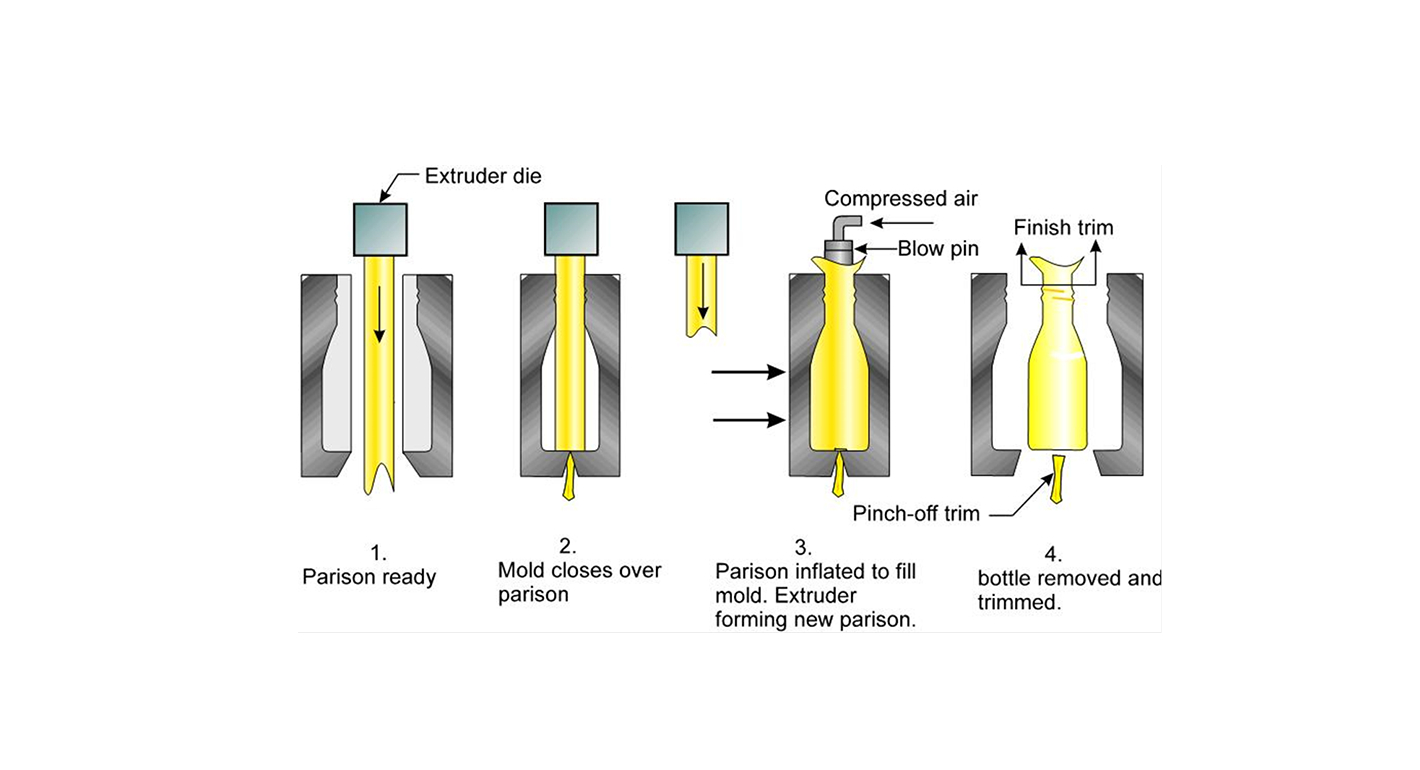
- Melted Polymer Injection: The process begins with the injection of melted polymer into the preform mold.
- Preform Creation: Subsequently, the polymer forms a preform, which has the same neck and thread as the final product but a simple cylindrical shape for the body.
- Cooling: The preform then cools and solidifies while still attached to the core rod.
- Automatic Transfer:
- Rotation Mechanism: After cooling, the preform, still on the core rod, is automatically rotated to the blow mold station. This rotation ensures a continuous and efficient workflow without manual handling.
- Blow Mold Station:
- Blow Molding: Once in the blow mold station, compressed air is introduced. Consequently, this air inflates the preform to take the shape of the blow mold cavity, forming the final product shape.
- Cooling: The newly formed product is then cooled while still on the core rod, ensuring it retains its shape.
- Ejection Station:
- Product Release: Finally, after cooling, the finished product is ejected from the core rod.
- Quality Control: The product undergoes quality checks before packaging, ensuring high standards.
Illustrations and Examples
Imagine a modern IBM machine producing water bottles. The preforms are injected, rotated to the blow mold station, and inflated into the bottle shape—all within the same machine. This integration eliminates manual transfer, reducing cycle time and increasing precision.
Advantages of Integrated IBM Machines
Furthermore, let’s consider the advantages of integrated IBM machines:
- Increased Efficiency: Automatic transfer and integrated steps reduce cycle times.
- Enhanced Precision: Minimizes errors due to reduced manual handling.
- Higher Output: Continuous operation boosts production rates.
Disadvantages of Integrated IBM Machines
However, despite these advantages, there are also some disadvantages:
- Complexity: The machinery is sophisticated and requires skilled operation and maintenance.
- High Initial Cost: Investment in advanced machines is significant.
- Space Requirements: Larger machines may need more factory floor space.
Pros and Cons of Advanced IBM
Pros
Moreover, let’s highlight the pros of advanced IBM:
- Automation: Reduces human error and increases consistency.
- Speed: Faster production cycles compared to traditional methods.
- Quality Control: Integrated quality checks ensure high standards.
Cons
On the other hand, here are the cons:
- Cost: High setup and maintenance costs.
- Skill Requirements: Operators need specialized training.
- Flexibility: Machines may be less adaptable to different product designs.
In conclusion, the evolution of injection blow molding into a fully integrated process on a single machine marks a significant advancement in manufacturing technology. By automating the transfer of preforms and maintaining them on the core rod, these machines achieve higher efficiency, precision, and production rates. Although the initial investment and complexity are considerable, the benefits in terms of speed, consistency, and quality make it a preferred choice for large-scale production of hollow plastic products.